The World Wide Web is the digital universe at your fingertips—but how does it really work? Let’s decode the web, one byte at a time!
Breaking Down the World Wide Web:
The World Wide Web (WWW) has revolutionized the way we connect, learn, and live. But
for many, it’s a mystery wrapped in code, jargon, and complexity. Fear not! In this
beginner’s guide, we’ll break down the web into digestible pieces, helping you
understand its core components and how it powers our digital lives.

What is the World Wide Web?
At its core, the World Wide Web is a collection of documents and resources, like
websites, linked together using the internet. Think of it as the digital library of
the world, where each page, image, or video is a "book" you can instantly access.
Key Components of the Web
1. Web Pages and Websites
A web page is a single document, like a page in a book. A website is a
collection of related web pages.
Example: A blog post (like this one) is a web page; the blog itself is the
website.
2. Web Browsers
Your gateway to the web! Browsers like Chrome, Safari, or Firefox let you view
and interact with web pages.
Fun fact: The first browser, WorldWideWeb, was created by Sir Tim Berners-Lee
in 1990.
3. URLs (Uniform Resource Locators)
Every web page has a unique "address" called a URL. For example,
www.example.com . Think of it as the GPS for the web.
4. HTTP/HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is how data is exchanged between your
browser and the server. HTTPS adds a layer of security with encryption.
5. Servers and Clients
Servers are like warehouses storing web content. Clients (like your browser)
request and fetch this content for you.
How Does It All Work?
1. You type a URL
When you enter a URL in your browser, you’re essentially telling it where to
look for a specific resource.
2. Browser sends a request
Your browser sends this request to a server using HTTP/HTTPS.

3. Server responds
The server finds the requested content and sends it back to your browser.
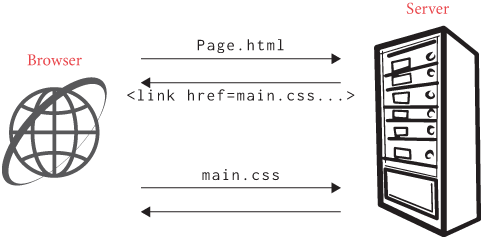
4. Page loads
Your browser processes the content (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and displays it as a
functional web page.

Understanding Web Technologies
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): The backbone of every web page, structuring
the content.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): Adds style and design to make web pages visually
appealing.
JavaScript: Brings web pages to life with interactivity and functionality.
Why Should You Understand the Web?
1. Empowerment: Knowledge of the web helps you navigate it confidently and safely.
2. Opportunities: From coding to creating content, understanding the web opens
doors in tech and beyond.
3. Digital Literacy: It’s a crucial skill in today’s interconnected world.
Ready to Dive Deeper?
Whether you want to explore web development, understand online security, or simply
demystify tech terms, this guide is just the beginning. The web may seem vast and
complex, but with a curious mind, you’ll navigate it like a pro.
So, the next time you click on a link, you’ll know exactly what’s happening behind the
scenes!
“The web isn’t just a tool—it’s a language of connection. Start decoding
it today!”